Saudi Arabian Oil Company, or Saudi Aramco, is the largest petroleum and natural gas company in the world in terms of revenue, market capitalization, and oil production. For over 90 years, it has been managing Saudi Arabia’s hydrocarbon resources. The management, integrity, and security of data are paramount, especially for industry mammoths like Saudi Aramco. However, despite implementing stringent security measures within the organization, the company was in the news in 2021 for facing a $50 million cyber extortion over leaked data. It was confirmed by the company that the data breach happened due to the negligence of the third party contractors rather than by the company. Saudi Aramco defines a third party as any external party that could be an individual, organization, or business generating, acquiring, compiling, transmitting, or storing data on Aramco’s behalf.
This case highlights the need for third-party vendors to adhere to cybersecurity controls and get certified with SACS-002 certification to fortify their defense mechanisms and prevent such breaches.
The third party cybersecurity compliance certification program ensures that the vendors working with Aramco adhere to the requirements mentioned in SACS-002 Third Party Cybersecurity Standard. This compliance certificate is also known as Aramco CCC and consists of the Cybersecurity Compliance Certificate (CCC) and the Cybersecurity Compliance Certificate Plus (CCC+). The vendor can attain these depending on their company classification:
|
Company Classification
|
Certificate Type
|
Assessment Approach
|
- General Requirements
- Outsourced Infrastructure
- Customized Software
|
Cybersecurity Compliance Certificate – CCC
|
A self-compliance assessment against SACS-002 is to be completed by the company and verified remotely by the Authorized Audit Firm.
|
- Network Connectivity
- Critical Data Processor
|
Cybersecurity Compliance Certificate Plus – CCC+
|
An on-site compliance assessment against SACS-002 is to be conducted by the Authorized Audit Firm.
|
Source: Saudi Aramco’s Cybersecurity Compliance Certification Third-Party Manual
If both certifications are applicable to any vendor based on the classification, then only CCC+ is accepted. Upon fulfilling all the applicable requirements of SACS-002, the company is provided the certification. If the company has not been able to obtain 100% compliance, then the authorized audit firm shares a non-compliance controls report, which needs to be implemented by the vendor. The compliance certificate is valid for two years, before the end of which the third-party company is required to submit a new certificate. In addition, if the third-party company has been awarded a new contract involving a cybersecurity classification type that is not covered in the present certificate, then a certificate needs to be obtained.
Third-Party Cybersecurity Standard (SACS-002)
SACS-002 Third-Party Cybersecurity Standard was issued by the Information Security Department of Saudi Aramco in February 2022. It is based on the NIST Cybersecurity Framework (NIST CSF). The standard delves into explaining the purpose, scope, cybersecurity control instructions, general & specific requirements, incident response instructions, audit mechanisms, etc., across IX sections and 3 appendices.
The purpose of the Third Party Cybersecurity Standard (TPCS) is to protect Saudi Aramco from possible security threats and enhance the cybersecurity posture of third parties. These third parties may deal with Saudi Aramco in varying capacities, such as providing a public cloud computing service to host data or processing critical data of Saudi Aramco customers. Such activities have been categorized into different classes, i.e., network connectivity, outsourced infrastructure, critical data processor, customized software, and cloud computing service.
At a minimum, the third parties need to comply with all the requirements specified in Section VII (A) - General Requirements of cybersecurity controls. For third parties that fall under any of the classes mentioned above, compliance with Section VII (B) - Specific Requirements is mandatory. The general requirements are divided into categories: identify, protect, and respond. The specific requirements are divided into categories: identify, protect, detect, and respond. To know the requirements of each cybersecurity control, refer to the Third Party Cybersecurity Controls Guideline.
Aramco's Third-Party Cybersecurity Controls
This document provides guidance to third parties working with Saudi Aramco to ensure that cybersecurity is managed in a uniform manner across entities and compliance requirements are met. This guideline must be utilized for both on-site and remote assessments. This guidelines document mentions cybersecurity controls, explaining clearly the requirements of each control. There are 92 cybersecurity controls in total. For the relevance of the article, controls related to media sanitization are explained below. SACS-002 defines ‘Sanitization’ as the process of permanent removal of data and software via overwriting or degaussing from an IT asset before it is loaned, transferred, surplused, donated, disposed of, or destroyed.
- TPC-19 (Data Sanitization): IT assets that are used to store or process Saudi Aramco data must be sanitized by the end of the retention period (if stated contractually) or by the end of the data lifecycle. This data also includes backup copies created at a third party site. The third parties must certify in written form that all the data has been sanitized.
Requirements of TPC-19:
- The third party must provide proof of third party sanitization policies.
- The third party must provide proof of sanitization techniques used. The procedures must be comparable to the security category, data or asset classification and comply with organizational standards & policies.
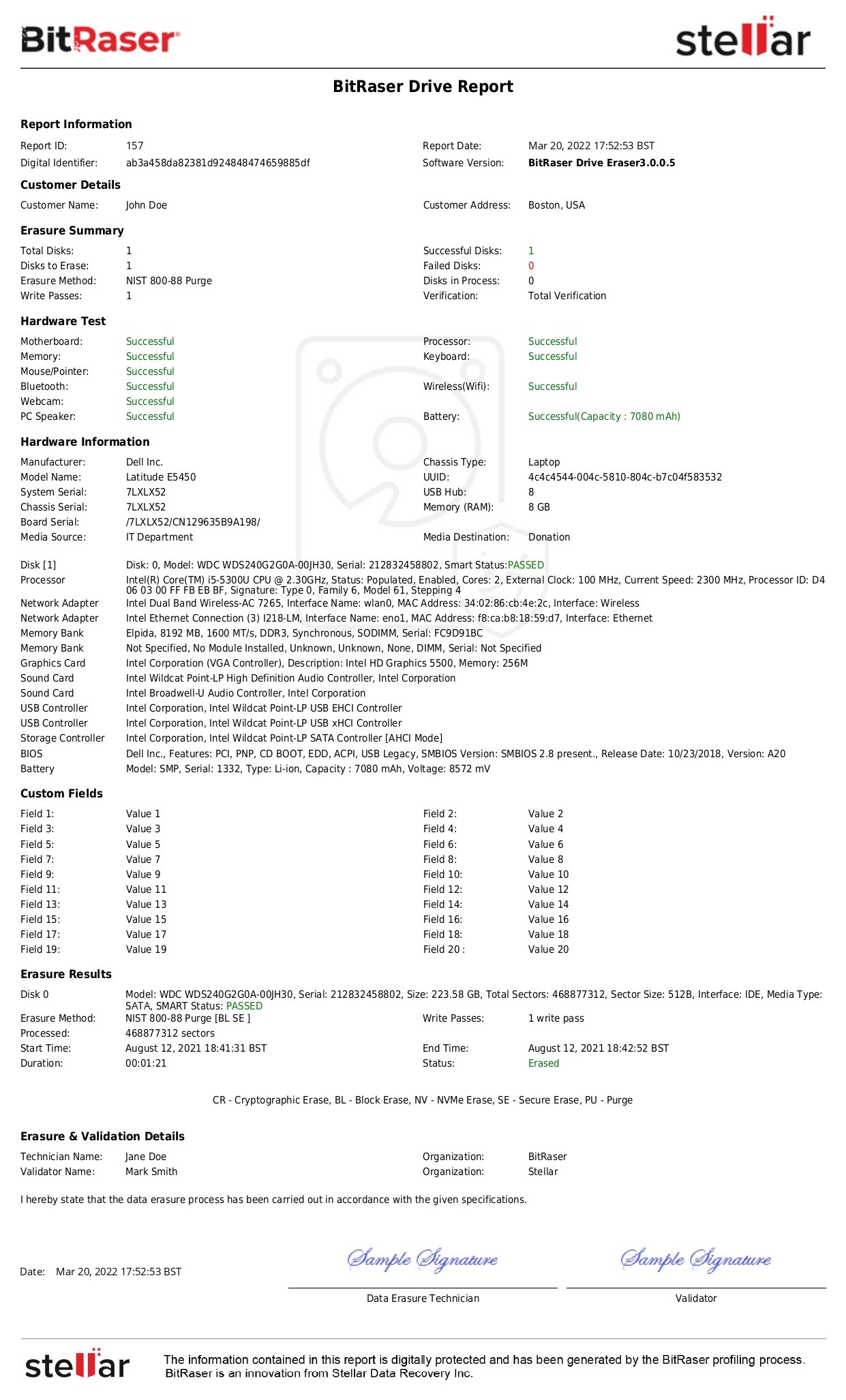
- The third party must provide evidence, like a certificate of destruction to prove that media sanitization took place as per the policy.
Note: Saudi Aramco vendors can rely on BitRaser Drive Eraser, a certified data erasure solution that permanently wipes sensitive data beyond recovery and generates a certificate of destruction, enabling third party organizations to comply with the SACS-002 standard.
- TPC-59: Mobile devices and tablets used to create, receive, and/or store critical data for Saudi Aramco must have a remote wipe solution installed on them.
Requirements of TPC-59:
- The third party must provide proof of the capability of data wiping remotely on mobile devices when missing or stolen data is enabled.
- It is also required to provide proof of policy related to remote access and remote wipe solutions used.
- TPC-66: Before any IT assets are transferred, loaned, donated, surplused, or destroyed, the third party must implement a sanitization process in alignment with industry best practices like NIST SP 800-88. NIST guidelines suggest three media sanitization methods: Clear, Purge, and Destroy. Clear applies logical sanitization techniques like READ and WRITE commands, Purge applies physical and logical sanitization techniques preventing data recovery, and Destroy applies physical destruction techniques, rendering data recovery and device reuse impossible. Clear and Purge sanitization methods include software-based data erasure or data wiping.
Note: BitRaser is a NIST-tested and approved software that supports NIST Clear, NIST Purge, and other sanitization methods to ensure data, once erased, is irrecoverable.
Requirements of TPC-66:
-
- The requirements of this control are similar to those of TPC-19 in terms of providing proof of media sanitization, techniques used, and certificate of destruction.
Conclusion
Vendors and contractors working with Saudi Aramco must comply with Aramco’s SACS-002 standard and get certified with Aramco CCC (Cybersecurity Compliance Certificate). They are obligated to adhere to robust media sanitization practices, which form a critical component of Aramco’s third party cybersecurity strategy. By proactively following the standards and guidelines explained above, third parties can significantly mitigate the risks of data breaches and stay compliant with Saudi Arabia’s Personal Data Protection Law (PDPL).