Summary: Data sanitization is critical for protecting businesses and individuals from data breaches and for meeting regulatory compliance. Degaussing and data erasure are two commonly used methods for sanitizing storage devices and drives. Learn how data erasure differs from degaussing and know about the limitations of degaussing in this article.
Degaussing and Data Erasure are methods for sanitizing the data storage media such as HDD, SSD, memory cards, etc. The primary purpose of media sanitization is to safeguard businesses & individual users from the risks of data breach & leakage.
Prevalent media sanitization methods are also devised in a way to help organization’s attain regulatory compliance with data protection laws, particularly when a storage media moves through a “secondary transaction” such as return of leased IT asset, devices refurbishment & reselling, reallocation, donation, or disposal. Government regulations, internal data security policies and industry standards with regard to data protection mandate the organizations to sanitize their data storage media prior to its reuse or disposal.
Though media sanitization techniques and standards may vary, the outcome is expected to be consistent— the data stored on a media should be impossible to recover by using any data recovery method or tool after the media has been sanitized. Let's evaluate Degaussing and Data Erasure, the two prevalent methods for sanitizing the media, and also compare their advantages and disadvantages.
What is Degaussing?
Degaussing is particularly used for sanitizing magnetic storage media such as magnetic disk, hard disk, and magnetic tapes. It involves use of a strong reverse magnetizing field generated using a degausser to neutralize the magnetic field orientation of the storage devices, thereby turning the stored data into an unreadable and irretrievable state. However, as per NIST SP 800-88 Guidelines, “traditional techniques such as degaussing (for magnetic media) become more complicated as magnetic media evolves, because some emerging variations of magnetic recording technologies incorporate media with higher magnetic force. As a result, existing degaussers may not have sufficient force to effectively degauss such media”. Further, degaussing renders the sanitized storage media unusable and leads to the generation of toxic e-waste.
Disadvantages & Limitations of Degaussing
Degaussing may look simple but is risky for business, particularly if seen in the context of reliability. Some disadvantages & limitations of degaussing are as below –
- Cannot Sanitize Flash Storage Media: Degaussing cannot erase data from electronic chips based on FLASH NAND technology including USB flash drives, solid state drives, and flash memory cards. As per NIST SP 800-88 Guidelines, “existing degaussers may not have sufficient force to degauss evolving magnetic storage media and should never be solely relied upon for flash memory-based storage devices or magnetic storage devices that contain non-volatile non-magnetic storage.”
- Renders the Degaussed Media Unusable: The degaussing technique relies on permanent & complete demagnetizing of the magnetic storage media to destroy the stored information. The process fundamentally neutralizes the magnetic field turning its coercivity to zero thus destroying its capacity to store data. The degaussed media cannot be reused and has therefore no utility and almost nil residual value from a monetization standpoint.
- Costly Means of Media Sanitization: The cost of using a Degausser is high, which is perhaps economically viable for sanitizing large volumes of magnetic media. A National Security Agency (NSA) Evaluated Products List (EPL)-listed degausser may cost upwards of US$18000 which could be expensive for most organizations esp. SMB from an OPEX standpoint. Also, the degausser, being a physical device, has limitations of utility; in most cases, you would need separate degaussers for sanitizing the media across the physically spread facilities, which will add up to the operating expenses.
- Generates E-Waste: The e-waste produced due to degaussing is one of the major sources of toxins and accounts for significant percentage of the total toxic e-waste.
What is Data Erasure?
Data Erasure technique is based on overwriting all the addressable storage locations on the media with binary pattern (non-sensitive data), thus rendering the stored data unrecoverable using any tool or method. Data erasure can sanitize magnetic media such as hard drives as well as flash memory-based storage media such as SSD and flash memory cards. The data erasure technique can be implemented by using a software which initiates read & write commands on a functioning device to overwrite the target data with non-sensitive data.
Data erasure based media sanitization approaches offer the following innate benefits:
- Sanitizes Magnetic & Flash Storage Media: Data erasure technique can sanitize solid state drives, flash drives, memory card & other flash storage media along with magnetic storage media such as hard drive. It equips individuals & organizations with a more comprehensive media sanitization solution.
- Allows Hardware Reuse & Resale: Data erasure uses the overwriting method of data destruction without hampering the core property of the storage media, thereby retaining the monetary value and functional aspects of erased hardware for further usage.
- Generates Zero E-Waste: Data erasure is an eco-friendly solution that serves the purpose of safe and reliable media sanitization without generating any kind of e-waste. It helps organizations fulfill their e-waste obligations.
The technique of data erasure, when implemented through a software utility, can offer more comprehensive & extended benefits. For instance, BitRaser, a professional data erasure software, offers the following key benefits:
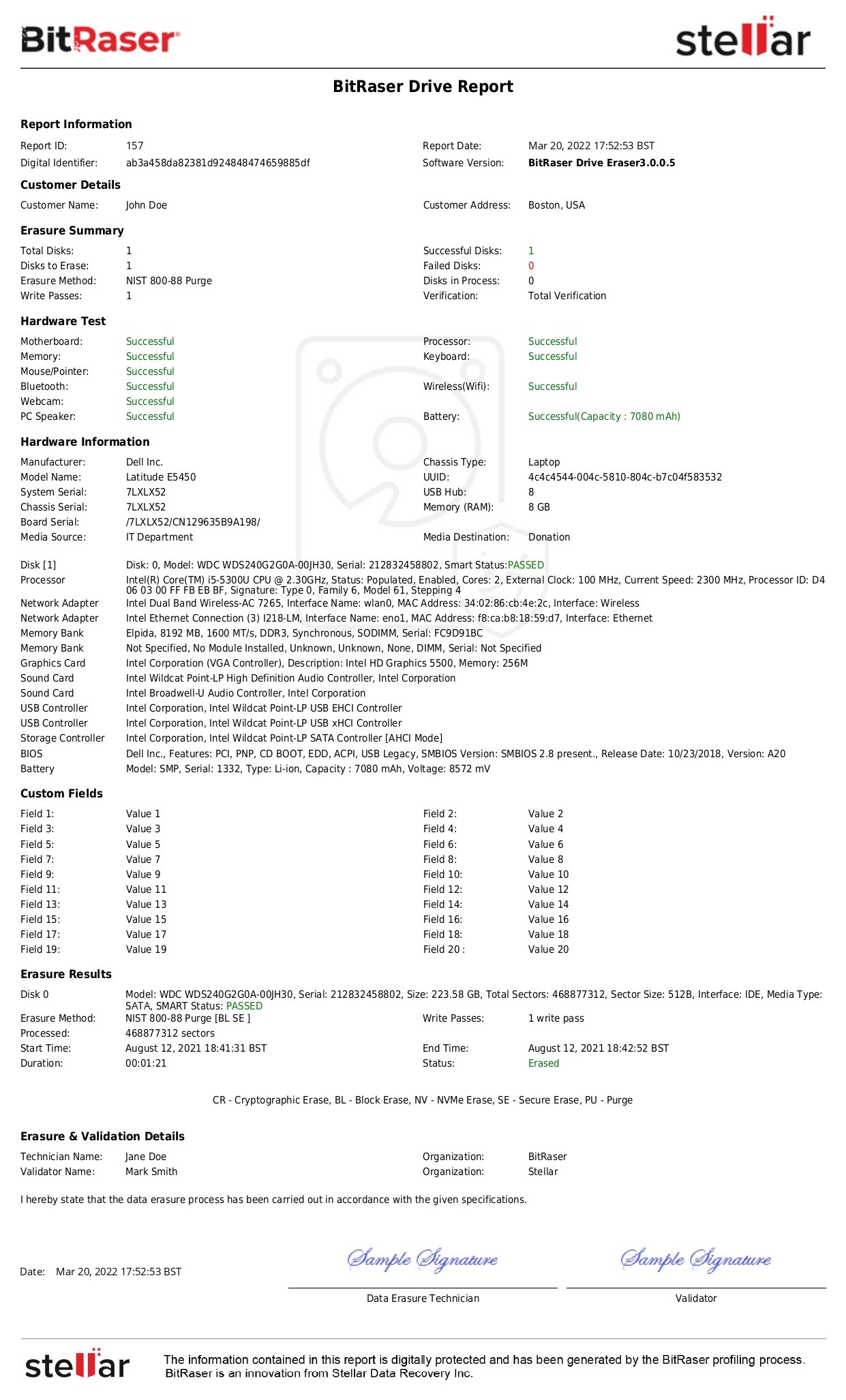
- Comprehensive Data Erasure as per Global Standards: Erases hard drives & SSDs used in laptops, desktops & rackmount storage. Also wipes Android and iOS devices. Supports NIST 800-88, DoD 5220.22-M & other 22 International erasure standards.
- Compliant Media Sanitization Solution: Generates automated reports and certificates of erasure that serve as immutable (tamperproof) audit trails for attaining 100% compliance with prevalent data protection regulations - GDPR, HIPAA, GLBA, SOX, and PCI-DSS.
- Logistic & Financial Viability: Centralized cloud-based delivery to erase drives & devices at physically spread out facilities with practically no logistic constraints & high manageability. Pay-per-use licensing for best value, based on the exact volume needs.
Data Erasure vs Degaussing – Quick Comparison
|
S. No.
|
Data Erasure
|
Degaussing
|
|
1
|
Suitable for all types of storage media including magnetic and non-magnetic storage. Can erase data from hard drives, USB flash drives, SSD, flash memory cards, etc.
|
Not suitable for flash memory based storage media including USB flash drives, solid state drives, and flash memory cards.
|
|
2
|
Software-enabled erasure can be scalable, as multiple devices can be erased simultaneously.
|
Degaussing is not scalable. Typically, a single drive is degaussed at a time.
|
|
3
|
More convenient and practicable as software-based erasure can be performed by a common IT user.
|
Requires a certain proficiency for operating the degausser viz. loading of the drive, degaussing, etc.
|
|
4
|
Erased media can be reused.
|
Degaussed media cannot be reused.
|
|
5
|
Cost-effective, as data erasure solutions are available with pay-per-use value licensing. Can be a shared cost as a single user account can be used to deploy erasure across global facilities.
|
High acquisition and operating costs that can incur separately for media sanitization in different facilities. Degausser being a hardware will depreciate in value over time.
|
|
6
|
Eco-friendly solution for media sanitization as data erasure produces zero e-waste.
|
Not eco-friendly, as degaussing generates a large amount of e-waste.
|
So, we now see the fundamental difference between data erasure and degaussing, the two well-known and widely used techniques of media sanitization. Aside from their contrasting utility, one aspect stands clear; data erasure can be a more effective, comprehensive, and reliable method for media sanitization, particularly when seen in context of the emerging storage media and need for compliance.
Other surrounding aspects i.e. hardware reusability, costing, ease-of-use, eco-friendliness, etc. also make data erasure a clear winner when it comes to choosing the best all-round media sanitization solution.